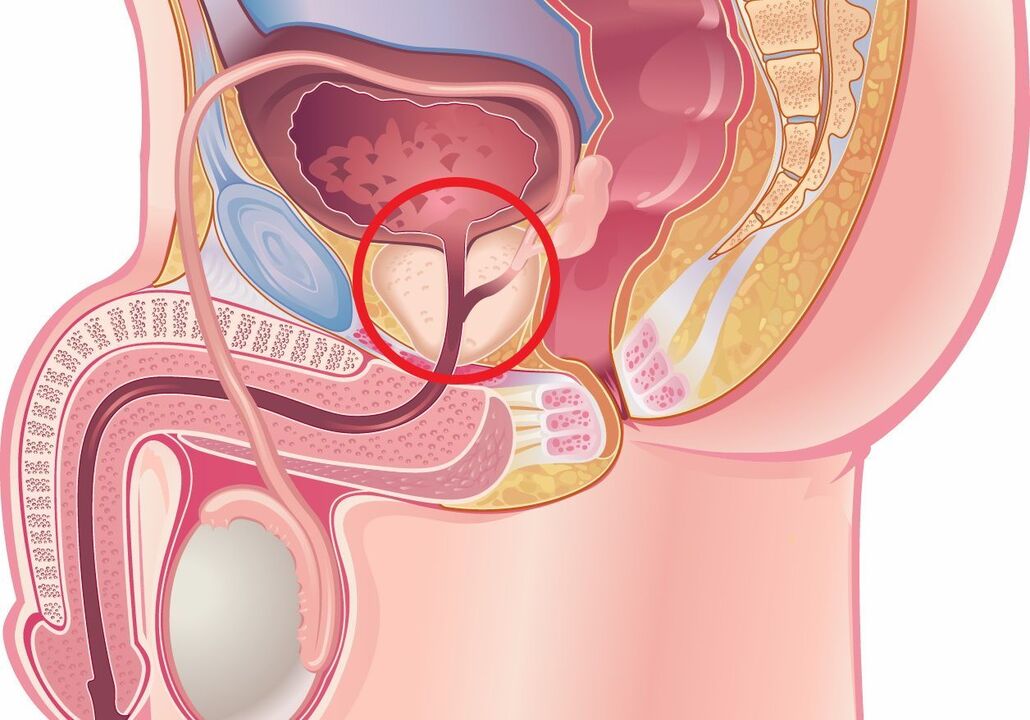
Congestive prostatitisis a pathological process in the prostate gland caused by swelling. Pathogenic flora is not detected, leukocytes can be detected by microscopy of prostate secretion, sperm and urine. Symptoms include constant aching pain in the perineum, dysuria. Diagnosis is based on the results of bacterial culture of biomaterial and TRUS. There is no single treatment regimen for congestive prostatitis; Massage, physiotherapy, antimicrobial drugs and alpha-blockers are prescribed. An individual approach is needed, taking into account the existing symptoms. If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgery is possible.
General Information
Prostatitis can be infectious, caused by the presence of pathogenic microflora, or stagnant, associated with blood congestion, retention of ejaculate and prostate secretion. Congestive or congestive prostatitis (vegetative urogenital syndrome, prostatitis) is an outdated name. Modern specialists in the field of urology more often use the term "chronic pelvic pain syndrome without inflammatory response" (CPPS). Prostatitis occurs in 25% of men aged 35-60, inflammation caused by congestive processes makes up 88-90% of all cases. A potentially congestive form of the disease supports pathogens that are in L-forms, fixed on biofilms, and not detected by routine methods.
Reasons
The causes of congestive prostatitis can be related to both the gland itself and extraprostatic factors. The exact etiology is unknown, probably due to stagnation of secretions in the prostate or venous congestion in the pelvic organs and scrotum. Some urologists consider this condition psychosomatic. The line between bacterial and bacterial inflammation is very arbitrary; With immunosuppression of any origin, due to the addition of secondary microflora, the process becomes infectious. Congestive prostatitis is caused by:
- Internal urological causes. Functional or structural pathology of the urinary bladder: cervical obstruction, inability to relax the external sphincter during bowel movements, detrusor contraction disorder contributes to urine retention and, due to the compression of blood vessels, blood stagnation. Prostatic hyperplasia and tumors, urethral stricture, and obstructive bladder stones are also considered potential causes of venous edema.
- compression. Blood flow is obstructed due to compression of the venous plexus by retroperitoneal tumors, metastases, and stool-filled bowel loops (stricture). The vessels of the ureteral plexus expand, blood circulation slows down, tissues experience oxygen starvation and are replaced by non-functional structures. Part of the blood is deposited and excluded from the circulation.
- behavioral factors. Abstinence from sexual activity, irregular ejaculation, and the use of interrupted intercourse as a means of preventing an unwanted pregnancy cause increased blood flow and swelling of the prostate tissue. During ejaculation, this gland does not fully dissolve. Constant masturbation can cause congestive prostatitis because. . . In order to develop an erection, it is necessary to get blood into the genitals.
Predisposing factors include low physical activity, hypothermia and overheating, poor diet with an excess of spicy, smoked foods. Alcohol and nicotine affect the tone of the vascular wall, disrupt redox processes and permeability, which causes swelling. Anomalies of the pelvic vascular system - valvular insufficiency, congenital weakness of the venous wall are considered to be the main prerequisites for the formation of congestive prostatitis affecting all organs of the male genital area (vesicles, testicles).
pathogenesis
The peripheral zone of the prostate consists of ducts that have a poorly developed drainage system, which prevents the outflow of secretions. As the prostate enlarges with age, patients develop urinary reflux into the prostatic ducts. It has been noted that many men with prostatitis are more prone to allergies. Scientists believe that such patients may be suffering from autoimmune-mediated inflammation caused by a previous infection.
Urinary reflux is caused by urethral stricture, bladder dysfunction, and BPH. Even the backflow of sterile urine causes chemical irritation and inflammation. Fibrosis of the ducts begins, prerequisites for prostatolithiasis are created, which increases intraductal obstruction and stagnation of secretion. Inadequate drainage of the acini causes an inflammatory reaction, the increase in swelling is accompanied by the appearance of symptoms. The condition is aggravated by blood swelling (stagnation) in the pelvis.
classification
The general classification of prostatitis includes acute (I) and chronic (II) bacterial forms. Category III includes subtype IIIa – CPPS with inflammation and IIIb – CPPS without it. Congestive prostatitis is considered a manifestation of CPPS in the absence of an inflammatory response (IIIb). There is a clinical differentiation that takes into account the pathogenetic and morphological features of the disease:
- the first stage.It is characterized by the predominance of processes of exudation, emigration, arterial and venous hyperemia, which leads to microvasculature damage and gland tissue destruction. These changes are recorded in the first years after the onset of the disease. The clinical picture is the most pronounced in the first stage.
- the second stage.The initial processes of connective tissue proliferation develop and symptoms decrease. Due to the formation of a blood clot, microcirculation is damaged, which aggravates sclerosis. At this stage, the majority of patients have sexual dysfunction: erection and orgasm intensity weaken, premature ejaculation develops, or on the contrary, it is difficult for a man to reach climax.
- The third stage. Severe fibrosclerotic changes are characteristic. It has been proven that the proliferation of connective tissue is stimulated not only by inflammation, but also by ischemia, which accompanies congestive prostatitis. Complaints of difficulty urinating are characteristic, and the involvement of the kidneys in the pathological process is noted.
Symptoms of congestive prostatitis
Pathology is manifested by various symptoms. Most patients describe the pain as constant discomfort in the perianal area, scrotum or penis. Some report increased perineal pain when sitting. The radiation of pain is variable - in the lower back, to the inner part of the thigh, on the tailbone. Swelling of the gland often makes it difficult to urinate and weakens the flow of urine. Inflammation of the congestive type against the background of vascular pathology is often accompanied by hemospermia - the appearance of blood in the semen.
Symptoms of bladder irritation include frequent urges and urinary incontinence. Depressive disorders develop with long-term pathology. It is still controversial whether psycho-emotional characteristics cause discomfort in the perineum or, on the contrary, pain caused by swelling of the prostate gland affects the mental state of men. An increase in temperature with a chill indicates the transition of bacterial congestive prostatitis to an infectious one and the need to start pathognomonic treatment.
Complications
Congestive prostatitis can become acute bacterial with the addition of microflora. Neighboring organs and structures may be involved in the inflammatory process: vesicles, bladder, testicles. The role of the prostate gland is to produce fluid for sperm; Usually it has a special composition that has a protective function for male germ cells. Insufficient amount of nutrients and changes in the biochemical properties of prostate secretion inevitably affect the quality of ejaculate; Men with congestive prostatitis are more often diagnosed with infertility.
With strong swelling of the organ, part of the urine remains in the bladder, which leads to pathological reflux of urine in the ureters and the collecting system of the kidneys. In response to reflux, hydronephrosis and permanent pyelonephritis with impaired kidney function may develop. 50% of men develop sexual dysfunction: painful ejaculation, dyspareunia, unpleasant night erection, which worsens the quality of life and negatively affects the relationship in a couple.
diagnosis
Determining the origin of symptoms is crucial for the effective treatment of congestive prostatitis, so various questionnaires have been developed to facilitate the diagnosis: I-PSS, UPOINT. These questionnaires are available in Russified form, they are used by urologists and andrologists in their practice. In order to rule out myofascial syndrome, consultation with a neurologist is indicated. On palpation, the prostate is enlarged, moderately painful, the nature of the disease is evidenced by varicose veins of the rectum. Diagnosis of congestive prostatitis includes:
- Laboratory testing. Microscopic and cultural examination of prostate juice is performed. Under the microscope, a slight increase in the number of leukocytes and negative results of bacterial culture confirm inflammation with bacterial congestion. PCR tests are performed to exclude the sexually transmitted nature of the disease. After the massage, the third part of the urine shows a more pronounced leukocyturia. Urine cytology can be performed to rule out bladder cancer, PSA blood test is justified in patients older than 40-45 years.
- Visual research methods. The main instrumental diagnostic method remains TRUS, bladder ultrasound. Cystourethrography results are informative in confirming bladder neck dysfunction, intraprostatic and ejaculatory reflux, and urethral stricture. In case of pronounced weakening of the jet, uroflowmetry is performed. Pelvic floor muscle tension is assessed using a videourodynamic study.
Differential diagnosis is carried out bladder carcinoma, BPH, interstitial cystitis. Similar manifestations are observed in tuberculosis of the genital organs and stricture of the urethra, since these nosologies are also characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, symptoms of dysuria and difficulty urinating. Congestive prostatitis is distinguished from bacterial prostatitis, in addition, all pathological processes accompanying CPPS in men should be excluded.
Treatment of congestive prostatitis
The patient is recommended to normalize his sexual life, because regular ejaculation helps to drain acini and improve microcirculation. Interrupted or prolonged intercourse that causes swelling is not allowed. A number of products have been identified that increase the chemical aggressiveness of urine - their consumption leads to an increase in the symptoms of congestive prostatitis. Spices, coffee, marinades, smoked foods, alcoholic and carbonated drinks should be limited, or even better excluded. Treatment of congestive inflammation of the prostate gland can be conservative and surgical.
conservative therapy
The treatment regimen is selected individually, depending on the prevailing symptoms. Many patients improve after receiving antibacterial drugs, which is explained by the incomplete diagnosis of latent infections. Alpha-blockers are prescribed for sluggish urine flow and the need to strain. The need to urinate is neutralized with anticholinergic drugs. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors have been shown to reduce the severity of clinical manifestations by reducing the response of macrophages and leukocytes and their migration to the inflamed area.
Pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants can help relieve pain and muscle spasm. It is advisable to include microcirculation normalizing drugs - phlebotonics (venotonics) in the treatment scheme. If the stagnation process contributes to androgen deficiency, they resort to hormone replacement therapy. Patients with anxiety-hypnotic and depressive disorders are advised to consult a psychiatrist who will select the optimal antidepressant.
With congestive inflammation of the prostate, physiotherapeutic procedures help to normalize men's health. They use laser and magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, etc. Sh. Spa treatments help to relieve symptoms of dysuria and improve sexual function: taking mineral water, paraffin and mud applications, massage showers. In some patients, there is a normalization of well-being during exercise therapy to reduce pelvic muscle tension. Prostate massage does not change natural ejaculation, but improves blood circulation and drainage of the organ.
Minimally invasive treatment methods
If conservative therapy has failed, high-tech interventions are considered - transurethral resection of the prostate, high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation. The most effective is transrectal hyperthermia - a non-invasive method based on the principle of thermal diffusion (the prostate is exposed to microwave energy). Heat increases tissue metabolism, reduces swelling symptoms and has a neuroanalgesic effect. Data on the effectiveness of treatment procedures for congestive prostatitis are limited.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for life is favorable, but chronic pelvic pain is difficult to treat. Sometimes congestive prostatitis disappears spontaneously over time. Long-term disturbance of blood circulation leads to sclerosis of the glandular tissue, which is manifested by the deterioration of the parameters of the spermogram. The prognosis of congestive prostatitis largely depends on the patient's adherence to all recommendations and lifestyle changes.
Prevention includes sports, lifting weights, normalizing sexual relations and avoiding coffee and alcohol consumption. When working in a sitting position, it is recommended to take breaks to perform physical exercises and use a pillow. Loose underwear and pants are preferred. Patients are monitored by a urologist with periodic evaluation of prostate secretions by inflammation and ultrasound examination, and receive antibacterial treatment and prostate massage sessions if necessary.



































